This article will take a deep dive into AR and VR, exploring their impact on customer interactions. We will see how to incorporate them into our content strategies, delivering enhanced experiences. Seamless content flow is vital to maintain a smooth customer journey, harnessing the power of AR and VR to create interactive spaces. By doing so, we position ourselves at the forefront of innovation and customer-centricity, unlocking their potential to transform interactions and shape the future.
AR and VR: Transforming Customer Engagement and Organizational Dynamics
Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) are cutting-edge technologies transforming customer experiences and internal processes within organizations. Let's dive into what these technologies are and explore their impact.Augmented Reality (AR)
AR is an innovative technology that blends computer-generated content into your real-world perspective. Unlike virtual reality (VR), AR enhances your environment without obstructing it. With various implementation methods, AR opens up a world of possibilities:- Smartphone or Tablet: By using your device's camera, AR applications can track your position and orientation, superimposing digital content in real-time.
- Head-Mounted Display (HMD): HMDs project digital images onto your eyes, allowing you to see both the real world and digital content simultaneously. A prime example of this technology is the HoloLens.
- Projectors: Projectors are used to display digital images on real-world surfaces, creating large-scale AR experiences.
The potential applications of AR are truly remarkable and diverse:
- Entertainment: Remember the Pokémon GO craze? AR is the key ingredient that lets you catch virtual creatures in the real world, making gaming more thrilling than ever.
- Education: Say goodbye to textbooks! With AR, students can explore interactive 3D models of their surroundings. For example, The New York Times AR app allows users to see augmented reality versions of news articles.
- Retail: Curious to see how that sofa will complement your living room? AR empowers you to visualize products in your environment, simplifying shopping decisions. Take IKEA, for instance, which allows customers to preview furniture in the comfort of their homes using AR technology.
- Manufacturing: AR comes to the rescue in the industrial world, guiding workers through intricate tasks and repairs. Just ask Boeing's technicians!
AR is continually evolving, promising even more innovative applications in the future.
How Do AR Solutions Work?
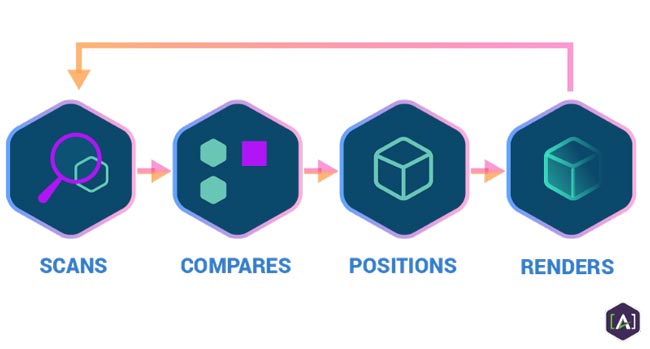
There are many different approaches to AR. Typically, the user sees live images of an object (product) through a mobile device (often a smartphone or tablet). The AR software on the device identifies and interprets live images by searching and comparing them with images stored in a local or remote database. Once matches are found, the AR device will simultaneously display or superimpose the digital content associated with a particular image.This process continues seamlessly as the user changes orientation or moves around and as new images (people, places, or objects) come within range of the sensors (in this case, a camera). Superimposed content seamlessly changes on an as-needed basis to match what the user is seeing.
A simplified definition of the technology and hardware components behind a typical AR solution includes these items:
- QR codes
- 2D image tracking
- 3D edge-based tracking
- Simultaneous Localization And Mapping (SLAM)
Virtual Reality (VR)
VR, on the other hand, offers a simulated environment that you can experience through a headset or similar devices. It provides an immersive encounter where computer-generated images and sounds captivate your senses, transporting you to a virtual world. Some popular applications of VR include:
- Entertainment: VR gaming takes realism to a whole new level, letting you become the protagonist of your adventure. Games like Half-Life: Alyx transport players to a realistic virtual world.
- Education: No need to imagine anymore! VR lets students explore 3D models and simulations, making learning engaging and unforgettable.
- Training: VR offers a safe and effective way to train individuals for real-world tasks. Pilots can practice flying without getting into an actual plane.
- Therapy: VR becomes a therapeutic tool, helping treat anxiety and post-traumatic stress disorder by exposing patients to feared situations in a controlled environment.
Similar to AR, VR keeps evolving with limitless potential for innovative applications.
Investigating the Landscape of Augmented Reality for Technical Communication
Augmented reality and Virtual reality are not all black goggles, gaming, and consumer applications. This emerging technology applies to more than you might think across the customer experience landscape.
In the customer experience and communication professions, our goal is to deliver the right content interactions as seamlessly as possible. Because augmented reality superimposes content over real-world environments, we are getting even closer to meeting users where they are in real-time. We create a bridge between our customer’s world and our own.
Ambitious sounding, but new modes of interaction gain adoption every single day. The rate at which both conversational interfaces and wearables have become part of our everyday lives has been astounding. With lower costs and improved technology, augmented reality is certainly on the same path.
With that said, organizations in the content space need to set a strategy for how to address this new delivery channel, with new content types, elements, and interactions.
We should proceed toward the future of customer experience intelligently, without constructing yet more content silos along the way. This mindset applies to any adaptive content experience including chatbots, personalized interactions, marketing automation, and new dimensional spaces.
AR and VR's Impact on Organizations
AR and VR are transforming how organizations operate internally. Some of the benefits of implementing these cutting-edge technologies are:
- Enhanced Training
- Elevated Customer Experiences
- Optimized Product Development
- Seamless Collaboration
- Effective Communication
- Reduced Costs
- Positive Customer Service
But the benefits don't stop there. According to PwC, AR, and VR have the potential to boost the global GDP by $1.5 trillion by 2030, with a significant portion attributed to increased worker productivity. As these technologies continue to evolve, businesses can expect even greater advantages and transformative opportunities.
Early adopters are already reaping the rewards and recognizing these technologies as indispensable tools that drive innovation and optimize internal processes. Research by Capgemini reveals that 46% of organizations using AR/VR reported a 10% improvement in operational efficiency. The impact of these technologies is real and makes a significant difference across various industries.
Crafting Immersive Experiences with [A]
Preparing for AR and VR content delivery comes with challenges and exciting opportunities. First and foremost, let's talk about the shift in mindset that content creators need to embrace. No longer is it just about creating content for publication; it's about crafting experiences that immerse customers. And we understand that this paradigm shift might call for learning new skills and approaches to content creation.
One of the first areas that need attention is updating schemas. These frameworks define the structure of content, and they must undergo a makeover to accommodate 3D models, spatial data, and interaction data to enhance the immersive experience. Content engineers must be at the forefront of this transformation, and familiarize themselves with new tools, techniques, and workflows specific to AR and VR content creation.
On the other hand, content creators, storytellers, and visionaries responsible for producing compelling content in the digital landscape must adapt content for the limited-screen real estate in these environments. Updating the governing schema or the Core Content Model® ensures that content seamlessly integrates into the immersive experiences.
[A] can be your strongest ally in constructing a Core Content Model® for VR/AR content. To deliver seamless and immersive experiences, [A] offers a comprehensive approach that harmonizes content across various tools and channels throughout its lifecycle.
[A]'s expertise tackles the task of addressing content silos and achieving a cohesive narrative. By implementing a Core Content Model® (CCM), [A] enables organizations to establish an enterprise-wide view of content assets, fostering consistency and coherence. This CCM approach facilitates content flow between different software applications, meeting the dynamic demands of the marketplace.
Together, [A] collaborates with content creators and content engineers to define the structure of content assets, enriching them with meaning and semantic value. With essential components such as the Content Relationship Diagram, Content Type Definitions, and supporting resources, [A] ensures an efficient and effective CCM. This helps content creators to gain a clear understanding of the organization’s content and automate processes for publishing and managing assets, as well as maintaining data accuracy.
The CCM model also provides organizations with increased flexibility. Content can be repurposed to meet new demands and support different use cases. By taking an agile approach to creating content, businesses can quickly produce content for a variety of digital channels. Additionally, they can ensure that content is consistent across all touchpoints.
The CCM model simplifies the complexities involved in managing large volumes of digital content and provides visibility into the entire process from creation to delivery. This allows teams to easily collaborate on content and drive innovation by creating new content quickly and efficiently. With the ability to reuse existing content, businesses can reduce costs and create more engaging experiences for their customers.
Ultimately, CCM provides organizations with a comprehensive approach to managing digital content across multiple channels. By taking a unified approach to creating and distributing content, teams can ensure accuracy, increase agility, and drive innovation. As a result, businesses can create more engaging customer experiences, improve efficiency, and increase profits. With CCM, organizations have the power to maximize their digital content efforts and stay ahead of the competition.
The CCM model also provides valuable insights into customer behaviors and preferences. By understanding what content resonates with customers, businesses can tailor content to specific audiences or channels. This helps ensure that content is optimized for maximum engagement and impact.
By taking a comprehensive approach to immersive content, businesses can capitalize on the immense growth opportunities that digital marketing presents. With the right tools and strategies, organizations can position themselves for success in an ever-evolving landscape.
Let us embark on this thrilling journey together, creating unforgettable storytelling experiences in the digital age. With [A] by your side, you can unleash the full potential of AR and VR, captivating your audience with engaging and informative content.
Acknowledgments
Thanks to Pontus Blomberg of 3D Studio Blomberg and Farhad Patel of Huawei for their time and insight.